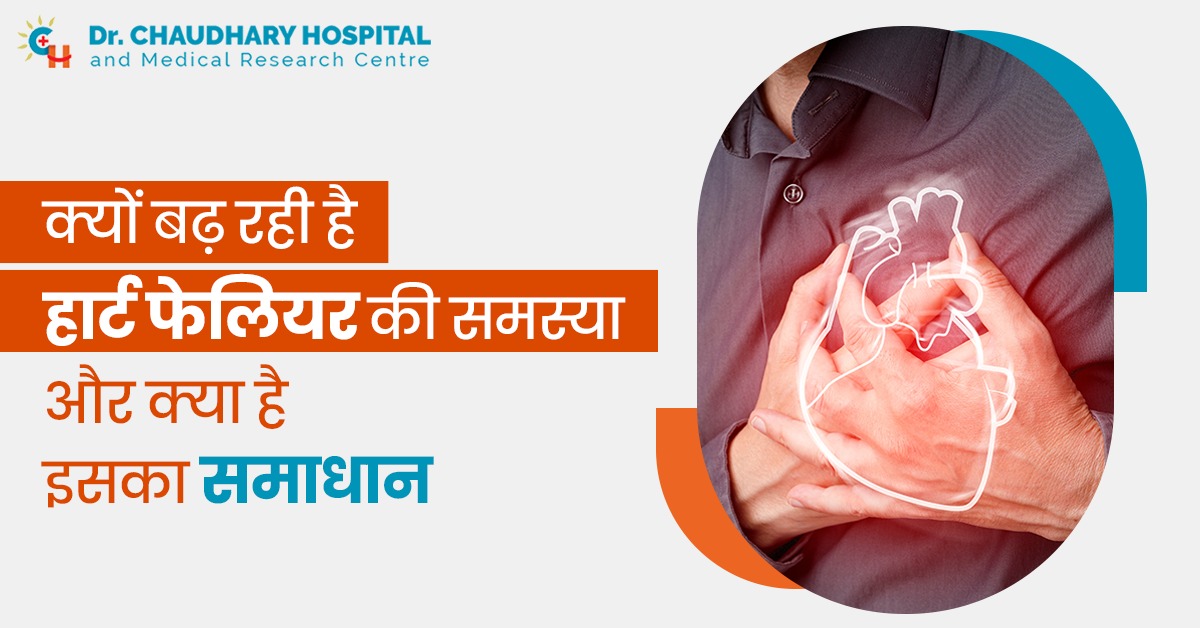
आज के समय में भागदौड़ भरी जीवनशैली में हार्ट फेलियर एक गंभीर समस्या के रूप में उभर रही है। भारत में हार्ट फेलियर की घटनाएं लगातार बढ़ रही हैं, और यह समस्या केवल बुजुर्गों तक सीमित नहीं है। युवाओं में भी इसके मामले देखे जा रहे हैं। बढ़ता तनाव, असंतुलित आहार, और शारीरिक गतिविधियों की कमी जैसी वजहें हार्ट फेलियर का कारण बनती जा रही हैं। इस लेख में हम हार्ट फेलियर की समस्या को विस्तार से समझने के साथ ही इसके लक्षण, कारण और समाधान के बारे में जानेंगे।
हार्ट फेलियर क्या होता है?
हार्ट फेलियर तब होता है जब हृदय की मांसपेशियां सामान्य तरीके से रक्त को पंप करने में असमर्थ हो जाती हैं। इसका मतलब यह नहीं कि हृदय पूरी तरह से काम करना बंद कर देता है, बल्कि इसका मतलब है कि हृदय कमजोर हो गया है और उतनी कुशलता से काम नहीं कर पा रहा है। यह स्थिति धीरे-धीरे विकसित होती है, और समय पर उचित उपचार न हो तो यह जानलेवा साबित हो सकती है।
हार्ट फेलियर के लक्षण
हार्ट फेलियर के लक्षण धीरे-धीरे बढ़ सकते हैं और आगे जाकर गंभीर हो सकते हैं। ऐसे में लक्षण दिखाई देने पर डॉक्टर से परामर्श अवश्य लें।
1. सांस लेने में कठिनाई : सामान्य गतिविधियों में भी सांस लेने में कठिनाई का अनुभव होना।
2. थकान : शरीर में ऊर्जा की कमी और सामान्य या बिना कोई काम किए थकान महसूस होना।
3. पैरों और एड़ियों में सूजन : खून का प्रवाह ठीक न होने से शरीर में फ्लूइड का जमाव हो जाता है। जिससे पैरों और एड़ियों में सूजन नजर आती है।
4. तेजी से वजन बढ़ना : शरीर में तरल पदार्थ के जमा होने से वजन में अचानक वृद्धि होती है।
5. अनियमित धड़कन : दिल की धड़कन में तेज़ी या असामान्य धड़कन महसूस होना।
हार्ट फेलियर के कारण
1. उच्च रक्तचाप : लगातार उच्च रक्तचाप या हाई ब्लड प्रेशर से दिल की मांसपेशियां कमजोर हो जाती हैं, जिससे हार्ट फेलियर की संभावना बढ़ जाती है।
2. धमनियों में रुकावट : दिल की धमनियों में रुकावट से खून का प्रवाह बाधित होता है, जिससे दिल को अधिक मेहनत करनी पड़ती है, और वह कमजोर हो जाता है।
3. डायबिटीज : डायबिटीज से भी हृदय पर नकारात्मक प्रभाव पड़ता है, और हार्ट फेलियर की संभावना बढ़ जाती है।
4. खराब लाइफस्टाइल: असंतुलित आहार, धूम्रपान, शराब का सेवन और तनावपूर्ण जीवनशैली भी हार्ट फेलियर के जोखिम को बढ़ावा देते हैं।
5. अन्य बीमारियां : थायरॉइड, किडनी फेलियर, या हृदय की अन्य बीमारियां भी हार्ट फेलियर का कारण बन सकती हैं।
हार्ट फेलियर का समाधान
हार्ट फेलियर का उपचार संभव है, लेकिन इसके लिए लक्षणों की समय पर पहचान और कुछ उपायों को अपनाने की आवश्यकता होती है। ये उपाय हार्ट फेलियर से बचाव और इलाज के जोखिम को कम करने मददगार साबित हो सकते हैं। यहां हम कुछ उपायों के बारे में जानेंगे।
1. लाइफस्टाइल में सुधार : हार्ट फेलियर से बचाव के लिए स्वस्थ जीवनशैली अपनानी चाहिए। जिसमें नियमित व्यायाम करना, संतुलित आहार लेना, और धूम्रपान-शराब का त्याग करना आदि शामिल हैं।
2. तनाव से बचें: तनाव का सीधा असर दिल की सेहत पर पड़ता है। ऐसे में किसी भी प्रकार का तनाव लेने से बचें। तनाव से बचाव के लिए योग एवं ध्यान अपनाएं।
3. दवाइयों का उपयोग : हार्ट फेलियर के मरीजों के लिए कई दवाएं उपलब्ध हैं, जो हृदय की कार्यक्षमता को सुधारने और लक्षणों को नियंत्रित करने में सहायक हैं। किसी भी प्रकार की दवाइयों का सेवन करने से पूर्व डॉक्टर से परामर्श अवश्य लें।
4. सर्जरी : यदि हार्ट फेलियर अत्यधिक गंभीर है, तो सर्जिकल विकल्प भी उपलब्ध होते हैं। इनमें बाईपास सर्जरी, हृदय प्रत्यारोपण, या पेसमेकर लगाना आदि शामिल हैं।
5. नियमित जांच : अगर आप भी हार्ट फेलियर के लक्षण महसूस करते हैं, या हार्ट संबंधी बीमारी से ग्रसित है तो नियमित जांच अवश्य करवाएं।
हार्ट फेलियर एक गंभीर समस्या है, लेकिन समय पर पहचान और जीवन शैली में सामान्य बदलाव कर इसे नियंत्रित किया जा सकता है। किसी भी प्रकार के उपायों को अपनाने से पूर्व डॉक्टर से परामर्श अवश्य लें।